Inflammatory Bowel Disease treatment
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treatment Services – Full Description
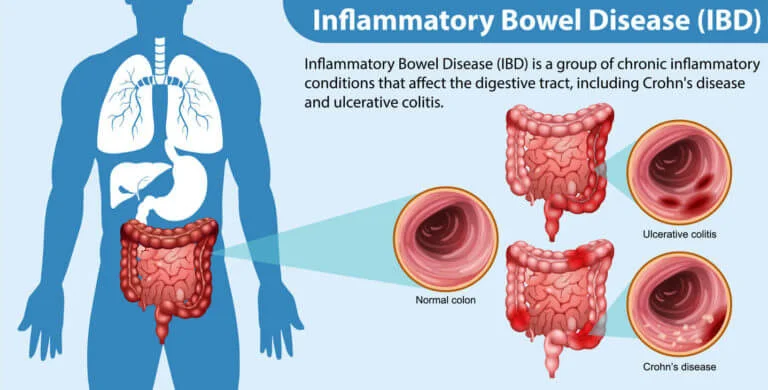
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) includes two main conditions:
-
Crohn’s Disease – Affects any part of the digestive tract from mouth to anus.
-
Ulcerative Colitis – Affects only the colon and rectum.
These are chronic conditions that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea (often with blood), fatigue, and weight loss.
1. Diagnostic Services
IBD diagnosis requires a combination of tests:
Lab Tests:
-
Blood Tests: To check for anemia and inflammation (CRP, ESR).
-
Stool Tests: To detect infections and inflammation (e.g., fecal calprotectin).
Endoscopic Procedures:
-
Colonoscopy with Biopsy: Main test to diagnose IBD and distinguish between Crohn’s and UC.
-
Upper GI Endoscopy: Used if upper tract symptoms are present.
Imaging:
-
CT/MRI Enterography: For small intestine inflammation in Crohn’s.
-
Ultrasound: For fast, non-invasive bowel assessment.
Other Evaluations:
-
Anorectal manometry or defecography (if bowel movement disorders are suspected).
2. Medical Treatment Services
IBD has no complete cure, but modern treatments help control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life.
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
-
5-ASA (Mesalamine) – Mild to moderate ulcerative colitis.
-
Corticosteroids – Short-term use for flares (Prednisone, Budesonide).
Immunosuppressive Drugs
-
Azathioprine, Methotrexate, 6-MP – Used to maintain remission.
Biologic Therapy (Advanced Treatment)
-
Anti-TNF: Infliximab (Remicade), Adalimumab (Humira)
-
Anti-integrins: Vedolizumab
-
IL-inhibitors: Ustekinumab
-
JAK inhibitors: Tofacitinib (especially in UC)
These target the immune system and are effective in moderate-to-severe IBD.
Supportive Medications
-
Antibiotics (for infections or abscesses in Crohn’s)
-
Iron, calcium, B12, and vitamin D supplements
-
Anti-diarrheal or anti-spasmodic medications
3. Nutrition & Lifestyle Services
Diet plays a key role in managing IBD symptoms.
-
Dietitian-guided meal planning: Low-residue or elemental diets during flares
-
Nutritional supplements: Protein, vitamins, minerals
-
TPN (Total Parenteral Nutrition): For severe Crohn’s with malabsorption
-
Stress management and psychological counseling: Helps reduce flare-ups
4. Surgical Treatment Services
Surgery is needed if there is:
-
Severe bleeding
-
Strictures (narrowing)
-
Fistulas or abscesses
-
Colon cancer risk
Common Surgical Options:
-
Colectomy (removal of colon) – Curative in Ulcerative Colitis
-
Bowel resection – For damaged areas in Crohn’s
-
Strictureplasty – Widening narrowed intestines
-
Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (J-pouch) – After colectomy in UC
Surgery is not a cure for Crohn’s, but helps manage complications.
5. Long-Term Monitoring & Care
Ongoing care is essential due to the chronic nature of IBD:
-
Regular colonoscopy for cancer screening
-
Blood and stool tests to monitor inflammation and side effects
-
Drug level and antibody monitoring (for biologics)
-
Pregnancy planning and fertility counseling (IBD-specific)
6. Hospital & Support Services
Most IBD treatment centers offer:
-
24/7 gastroenterologist access during flares
-
Biologic infusion centers (in-clinic injections/IV biologics)
-
Emergency care for severe symptoms
-
IBD clinics with multi-specialty teams (gastroenterologist, surgeon, dietitian, psychologist)
-
Insurance & cashless claim support
-
Online consultations and medication reminders
